1 南京邮电大学电子与光学工程学院,柔性电子(未来技术)学院,江苏 南京 210023
2 东南大学电子科学与工程学院,江苏 南京 210096
提出一种外泌体检测新方法,通过将表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)纳米探针固定在核酸适体(DNA)功能化水凝胶中,实现对肿瘤源性外泌体的高灵敏度光学检测。SERS纳米探针被用于识别肿瘤源性外泌体并产生指纹光学信号。SERS活性DNA功能化水凝胶(简称“SD水凝胶”)作为传感器,不仅提供了用于生物识别的三维反应位点,而且可放大SERS纳米探针的光学信号。选择性地与靶外泌体结合后,SERS纳米探针脱离SD水凝胶,导致SERS信号减弱,从而实现光学检测。通过SERS信号变化,SD水凝胶可以定量、灵敏地检测肿瘤源性外泌体,浓度检测限(LOD)约为22 μL-1。该SD水凝胶将为临床癌症诊断提供一种新的技术手段。
生物光学 表面增强拉曼散射光谱技术 光学检测 外泌体 纳米探针 水凝胶 光学学报
2023, 43(21): 2117001
利用金属有机化学气相沉积方法在蓝宝石衬底上生长了一系列具有双中温AlN插入层(MTGAlN)的半极性AlN薄膜样品。中温生长的AlN插入层具有较大的表面粗糙度,形成了类似纳米级图形化衬底结构,能够有效阻断高温生长的半极性AlN样品中堆垛层错的传播,从而提高半极性AlN样品的表面形貌和晶体质量。通过原子力显微镜和X射线衍射仪的表征,研究了MTGAlN插入层厚度在20~100nm之间的变化对半极性AlN样品的表面形貌和晶体质量的影响。结果表明,所有半极性AlN样品都具有[1122]取向。当插入的MTGAlN中间层厚度约为80nm时,半极性AlN样品表面粗糙度显著降低,晶体质量明显改善。
双中温AlN插入层 半极性AlN 表面形貌 晶体质量 dual moderatetemperaturegrown AlN interlayer semipolar AlN epilayer surface morphology crystalline quality
采用金属有机化学气相沉积技术,在半极性蓝宝石衬底上成功生长了具有高电子浓度和良好表面形貌的Si掺杂的非极性a面nAlGaN外延层。深入研究了铟(In)表面活性剂和无掺杂的AlGaN缓冲层对nAlGaN的结构特征和电学性能的影响。表征结果表明,利用In表面活性剂和无掺杂的AlGaN缓冲层,非极性a面nAlGaN外延层的晶体质量的各向异性被有效地抑制,同时显著改善了其表面形貌和电学性能。测得非极性a面nAlGaN的电子浓度及电子迁移率分别为-4.8×1017cm-3和3.42cm2/(V·s)。
非极性a面nAlGaN 表面活性剂 AlGaN缓冲层 电学性能 nonpolar aplane nAlGaN indium surfactant AlGaN buffer layer electrical properties
1 东南大学电子科学与工程学院,江苏 南京 210096
2 中国人民解放军陆军装备部驻无锡地区军事代表室,江苏 无锡 214000
硅基探测器具有稳定可靠、暗电流低、响应度高、价格低廉等优点,被广泛应用于光电探测等领域。针对硅基探测器在紫外波段探测能力有限的问题,设计了一款可增强硅基探测器在紫外波段探测能力的聚光结构。首先,利用ZnCdS∶Mn/ZnS量子点的荧光特性将吸收的紫外光转化为可见光。然后,配合短波通截止滤色膜使探测器在260~400 nm波段的外量子效率均大于20%,响应时间限制在ms量级,暗电流限制在pA量级。实验结果表明,使用量子点层的聚光结构能明显改善硅基探测器在紫外波段的探测能力,通过改变量子点的尺寸还可以在紫外波段实现探测范围可调的硅基探测器。
探测器 外量子效率 掺杂量子点 短波通截止滤色膜 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(17): 1704001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
Photonic structures with topological edge states and resonance loops are both important in optical communication systems, but they are usually two separate structures. In order to obtain a photonic system combining properties from both, we design multiple-layer nested photonic topological structures. The nested topological loops not only have topological protection immune to structural disorder and defects, but also possess both the properties of unidirectional propagation and loop resonance. Through mode analysis and simulations, we find that the transport can form diverse circulation loops. Each loop has its own resonance frequencies and can be solely excited in the nested layered structure through choosing its resonance frequencies. As a result, this work shows great application prospects in the area of reconfigurable photonic circuits.
topological edge states unidirectional propagation loops resonance reconfigurability Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(6): 061301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology of Jiangsu Province, School of Physical Science and Technology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, China
3 School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410012, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
We investigate femtosecond laser trapping dynamics of two-photon absorbing hollow-core nanoparticles with different volume fractions and two-photon absorption (TPA) coefficients. Numerical simulations show that the hollow-core particles with low and high-volume fractions can easily be trapped and bounced by the tightly focused Gaussian laser pulses, respectively. Further studies show that the hollow-core particles with and without TPA can be identified, because the TPA effect enhances the radiation force, and subsequently the longitudinal force destabilizes the trap by pushing the particle away from the focal point. The results may find direct applications in particle sorting and characterizing the TPA coefficient of single nanoparticles.
laser trapping multiphoton processes ultrafast nonlinear optics Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(8): 081901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410012, China
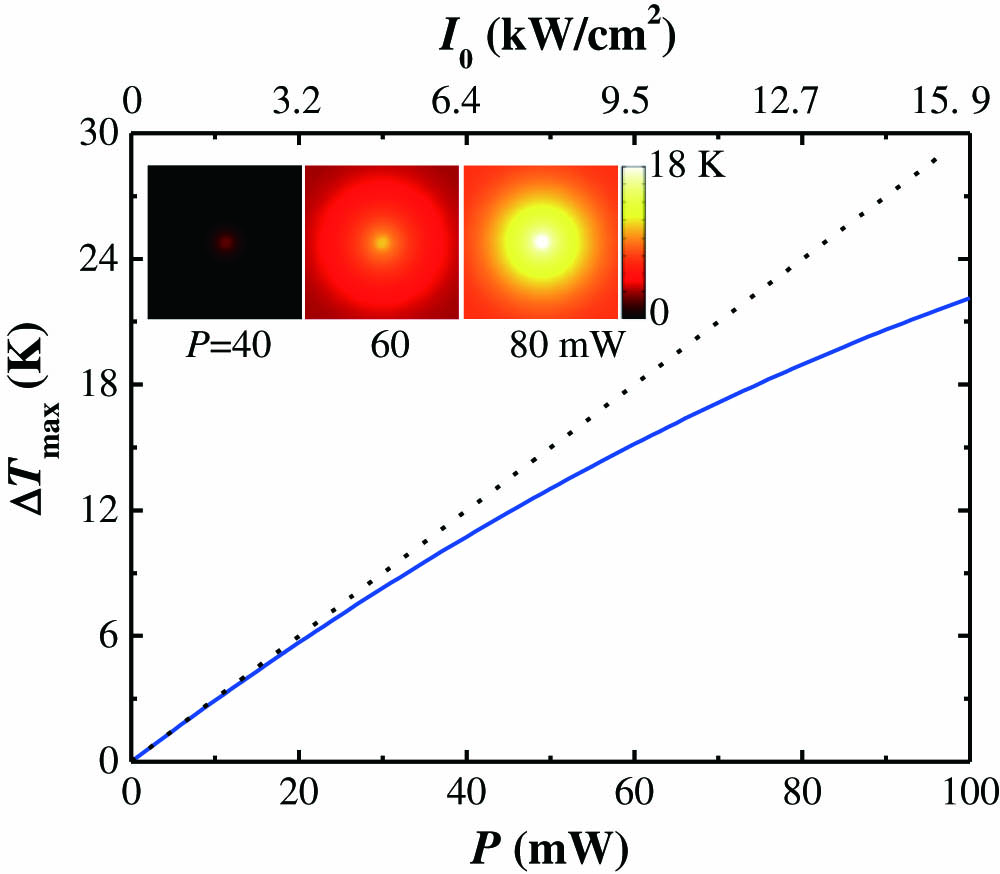
Understanding the nonlinear optical effect of novel materials plays a crucial role in the fields of photonics and optoelectronics. Herein, we theoretically and experimentally investigate the simultaneous presence of third-order locally refractive nonlinearity and thermally induced nonlocal nonlinearity saturation. We present analytical expressions for the closed-aperture Z-scan trace and the number of spatial self-phase modulation (SSPM) rings, which allows one to unambiguously and conveniently separate the contributions of local and nonlocal nonlinear refraction in the case that both effects occur simultaneously. As a test, we study both the local and thermally induced nonlocal nonlinear refraction in fullerene/toluene solution by performing continuous-wave Z-scan and SSPM measurements at two different wavelengths. This work enriches the understanding of the physical mechanism of the optical nonlinear refraction effect in solution dispersions of nanomaterials, which can be exploited for nonlinear photonic devices.
190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in 190.4870 Photothermal effects Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 061901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 Department of Electro-Optics and Photonics, University of Dayton, Dayton, Ohio 45469, USA
3 School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
4 e-mail: cyp@seu.edu.cn
5 e-mail: qzhan1@udayton.edu
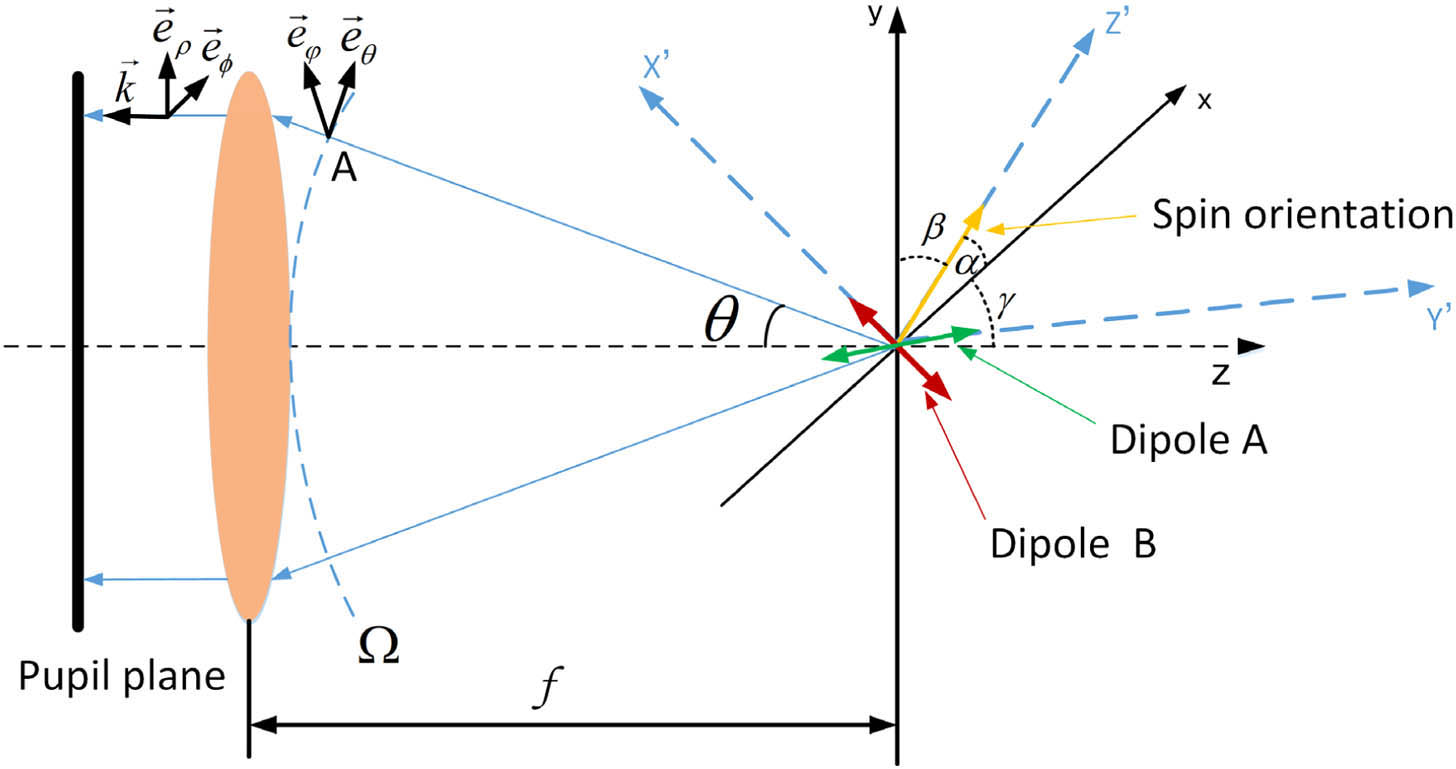
Optical trapping techniques hold great interest for their advantages that enable direct handling of nanoparticles. In this work, we study the optical trapping effects of a diffraction-limited focal field possessing an arbitrary photonic spin and propose a convenient method to manipulate the movement behavior of the trapped nanoparticles. In order to achieve controllable spin axis orientation and ellipticity of the tightly focused beam in three dimensions, an efficient method to analytically calculate and experimentally generate complex optical fields at the pupil plane of a high numerical aperture lens is developed. By numerically calculating the optical forces and torques of Rayleigh particles with spherical/ellipsoidal shape, we demonstrate that the interactions between the tunable photonic spin and nanoparticles lead to not only 3D trapping but also precise control of the nanoparticles’ movements in terms of stable orientation, rotational orientation, and rotation frequency. This versatile trapping method may open up new avenues for optical trapping and their applications in various scientific fields.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(1): 01000069

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, Jiangsu, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology of Jiangsu Province, School of Physical Science and Technology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, China
3 Department of Electro-Optics and Photonics, University of Dayton, 300 College Park, Dayton, Ohio 45469-2951, USA
The principle of optical trapping is conventionally based on the interaction of optical fields with linear-induced polarizations. However, the optical force originating from the nonlinear polarization becomes significant when nonlinear optical nanoparticles are trapped by femtosecond laser pulses. Herein we develop the time-averaged optical forces on a nonlinear optical nanoparticle using high-repetition-rate femtosecond laser pulses, based on the linear and nonlinear polarization effects. We investigate the dependence of the optical forces on the magnitudes and signs of the refractive nonlinearities. It is found that the self-focusing effect enhances the trapping ability, whereas the self-defocusing effect leads to the splitting of the potential well at the focal plane and destabilizes the optical trap. Our results show good agreement with the reported experimental observations and provide theoretical support for capturing nonlinear optical particles.
Kerr effect Laser trapping Particles Ultrafast nonlinear optics Photonics Research
2018, 6(2): 02000138





